Introduction
APEX Application Settings offer a convenient way to store values specific to an APEX Application. APEX Application Settings are configured in APEX Builder under Shared Components > Application Settings.
This post will describe how Application Settings work and how you can get and set values for them using the APEX_APP_SETTING PL/SQL API.
Use Cases
APEX Application Settings are helpful because they can be used to store Application specific values that can be updated via APEX Builder or a PL/SQL API. These capabilities allow you to expose settings that would usually be treated as constants, provide visibility to them, and update them under appropriate circumstances. APEX Application Settings have many uses, including:
- Storing application default values
- Indicating if features are enabled for an application
- Storing URLs to Web Service endpoints
Creating an Application Setting
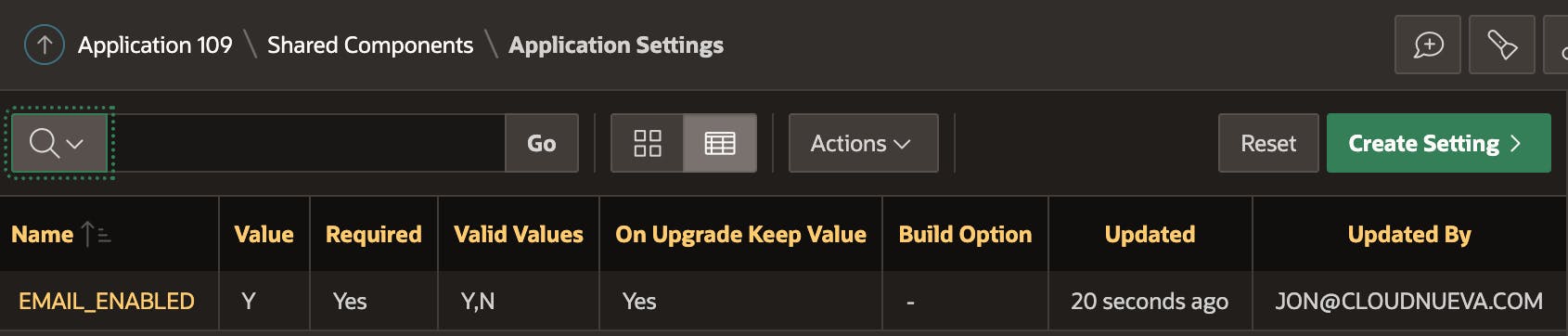
Let's start by creating an Application Setting. After Navigating to Shared Components > Application Settings, click the 'Create Setting >' button.
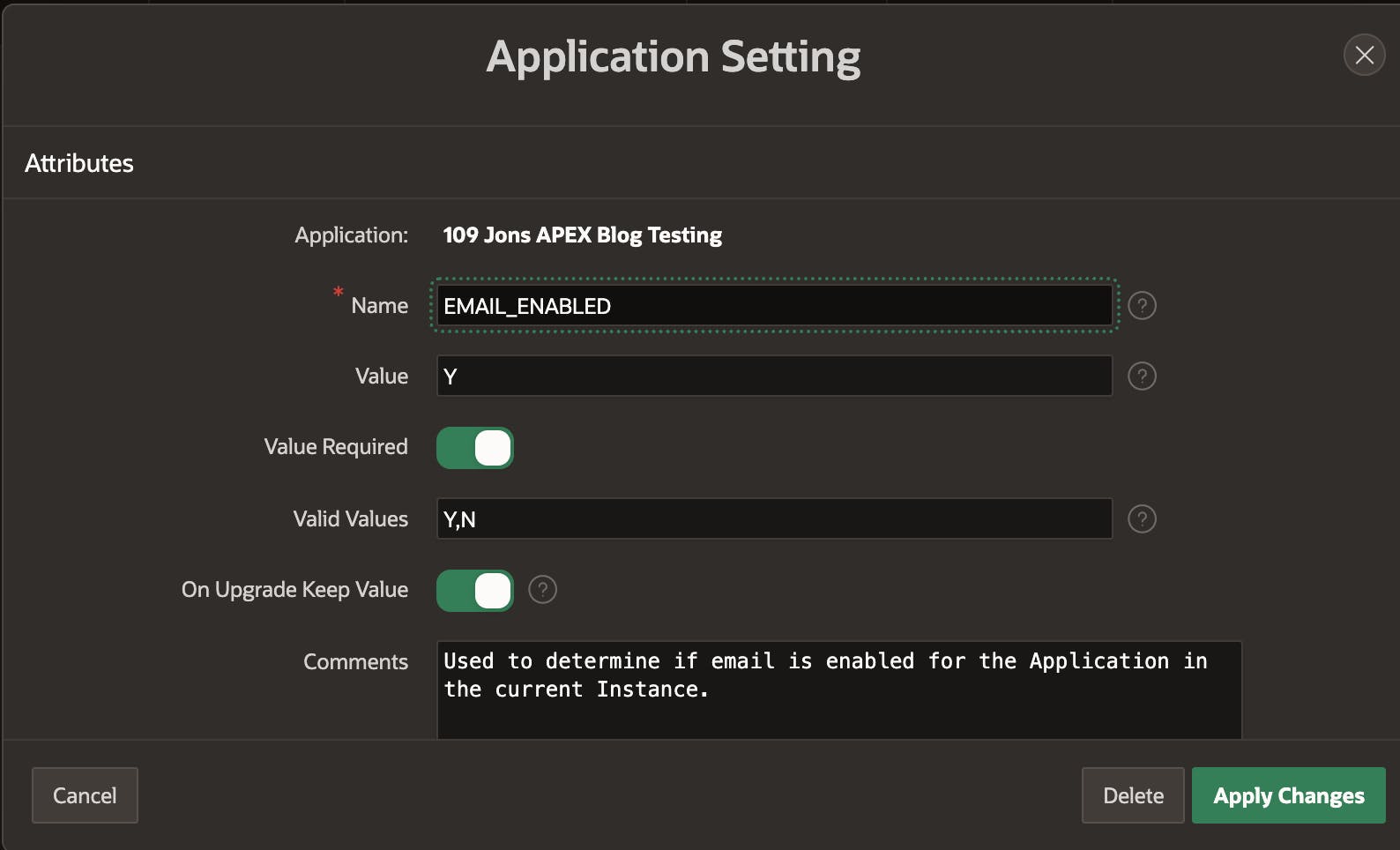 Let's examine the attributes in more detail:
Let's examine the attributes in more detail:
Name- The name for the Application Setting
- This name is also used when referencing an Application Setting from the PL/SQL APIs
Value- The current value for the Application Setting
- This can be anything you want
Value Required- Determines if a value is required for the Application Setting
Valid Values- A comma-separated list of allowed values for the Application Setting
- These values are enforced by the UI and by the PL/SQL APIs
- If this attribute is left empty then validation is not performed
On Upgrade Keep- See the section 'What Happens During Deployment' for details on this attribute
What Happens During Deployment
So, what happens when you deploy an application with an Application Setting? The behavior is governed by the attribute On Upgrade Keep. 💡I wish this attribute had been named On Deployment Keep Value.
If On Upgrade Keep is on for an Application Setting:
- If you deploy the Application and the Application Setting already exists in that Application in the target instance: the Application Setting value is not changed in the target instance
- If the Application Setting did not exist in the target instance: the Application Setting is created with the value from the source instance
If On Upgrade Keep is off for an Application Setting:
- If you deploy the Application and the Application Setting already exists in that Application in the target instance: the Application Setting value is updated in the target instance to match the value from the source instance
- If the Application Setting did not exist in the target instance: the Application Setting is created with the value from the source instance
APEX_APP_SETTING PL/SQL APIs
The APEX_APP_SETTING PL/SQL APIs help us interact with Application Settings from PL/SQL. Note: You must have an APEX Session established to call these APIs. Requiring an APEX session means if you are calling these APIs outside of APEX, you must first call apex_session.create_session or apex_session.attach.
Getting a Value via PL/SQL
The apex_app_setting.get_value function is simple to use.
DECLARE
l_email_enabled VARCHAR2(1);
BEGIN
-- Create an APEX Session (required if not calling from APEX)
apex_session.create_session
(p_app_id => 109,
p_page_id => 1,
p_username => 'CNDEMO');
-- Get the Application Setting Value.
l_email_enabled :=
apex_app_setting.get_value
(p_name => 'EMAIL_ENABLED',
p_raise_error => TRUE));
-- Clean up the APEX Session (only required if apex_session.create_session) is used
apex_session.delete_session ();
END;
Exceptions
If you set p_raise_error to TRUE (this is FALSE by default), then you can expect the following exceptions:
- No APEX Session Established
- ORA-20001: Package variable g_security_group_id must be set
- Invalid Setting Name
- ORA-20987: APEX - Requested Application Setting #XEMAIL_ENABLED# is not defined
Setting a Value via PL/SQL
As we can see from the below example, setting the value for an Application Setting is equally simple.
BEGIN
-- Create an APEX Session (required if not calling from APEX)
apex_session.create_session
(p_app_id => 109,
p_page_id => 1,
p_username => 'CNDEMO');
-- Set the Application Setting Value.
apex_app_setting.set_value
(p_name => 'EMAIL_ENABLED',
p_value => NULL,
p_raise_error => TRUE);
-- Clean up the APEX Session (only required if apex_session.create_session) is used
apex_session.delete_session ();
END;
Exceptions
If you set p_raise_error to TRUE (this is FALSE by default), then you can expect the following exceptions:
- No APEX Session Established
- ORA-20001: Package variable g_security_group_id must be set
- Invalid Setting Name
- ORA-20987: APEX - Requested Application Setting #XEMAIL_ENABLED# is not defined
- The value you are trying to set is not in the list of
Valid Values- ORA-20987: APEX - Application Setting EMAIL_ENABLED value is invalid
- The Attribute
Value Requiredis set on, but you are not passing a value- ORA-20987: APEX - Application Setting EMAIL_ENABLED may not be set to a null value
Conclusion
APEX Application Settings are a valuable tool in the APEX developer's toolbox. If you need to store Application wide settings and need the ability to allow them to be viewed or updated from your APEX Applications, then I encourage you to try them out.
Please also check out my other APEX posts:
- 🩳 APEX Shorts
- #️⃣ APEX Posts